what two words are used to classify epithelium in terms of the number of cell layers
Achieve Mastery of Medical Concepts
Table of Contents
Epithelial Tissue
Surface epithelium
A complex of specialized cellular organizations arranged into sheets and lining cavities and roofing the surfaces of the body:
- Derived from all 3 germ layers:
- Ectoderm (e.g., epidermis)
- Mesoderm (e.1000., GI tract lining)
- Endoderm (e.m., linings of body cavities)
- One of 4 major bones tissue types (the other 3 include nervous, muscular, and connective tissues)
These cells exhibit polarity:
- Apical/luminal pole: derived from the apex, faces the surface/lumen
- Basal pole: derived from the base, fastened to the connective tissue located below the epithelium
The surface epithelium does not possess blood vessels; therefore, nutrients and oxygen are received from side by side connective tissue.
Functions
- Protection (provides roofing surface or lining)
- Secretion (release of hormones, sweat, mucus, and enzymes) equally found in glands
- Absorption (substance intake equally seen in the intestinal lining)
- Excretion and filtration of substances
- Sensory reception (detection of awareness) equally found in olfactory epithelium
Related structures
- Intercellular junctions:
- Adhesion of cells is facilitated by cadherins (calcium-dependent adhesion molecules).
- At the apical finish, structures encircle the area (like a band around the prison cell):
- Tight or occluding junctions (zonulae occludens): have tight ridges, preventing passive flow of substances between cells
- Adherent junctions (zonulae adherens): assistance stabilize both junctions and hold cells together.
- Desmosomes (macula adherens) and gap junctions (communicating junctions):
- Structures bound to intracellular intermediate filaments, aiding the zonulae adherens
- Additionally, gap junctions permit flow of molecules.
- Hemidesmosomes: anchor epithelial cells to the basal lamina (of the basement membrane)
- Interdigitations: prison cell membrane foldings that increase the surface area (east.g., for ion or water transport)
- Basement membrane:
- Thin semipermeable sheet on which the basal surface of epithelia rests
- Attachment of cells achieved with laminin and integrin
- Parts:
- Basal lamina: thin, sheetlike layer of fine fibrils found nearest the epithelial cells
- Reticular lamina: thicker and more than fibrous
- Function:
- Zipper to underlying tissue
- Separation of tissues
- Filtration
- Scaffold and guidance (repair)
- Cell signaling
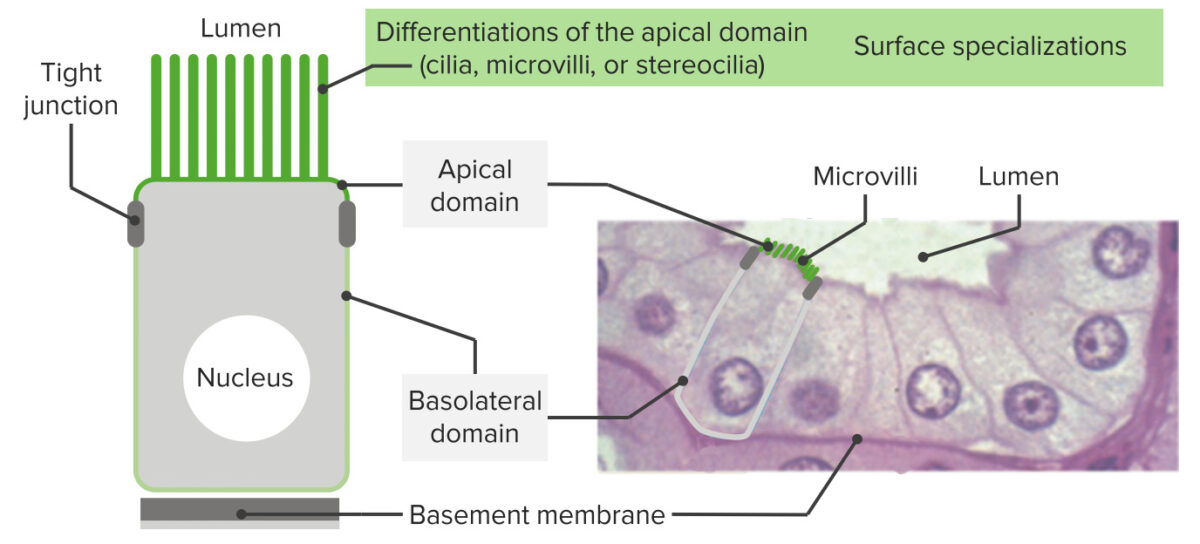
Epithelia have an apex, lateral borders, and a surface sitting on a basement membrane:
Equally seen in the image, these cells exhibit polarity (accept apical domains and basal/basolateral domains). At the upmost end, structures encircle the expanse (like a band around the cell) facilitating cell-to-prison cell adhesion (tight junctions and adherent junctions). Most the basement membrane, hemidesmosomes anchor the epithelia to the basal lamina. On the correct is shown the histology of the intestinal epithelial lining with corresponding structures. On the apical domain, microvilli are seen.
Classification
By number of layers
- Simple epithelium:
- Consists of a single layer
- Typically found where absorption, secretion, and filtration occur
- Stratified epithelium:
- Composed of ≥ 2 layers
- Found in high-abrasion areas (skin and lining of the mouth)
- Name of cells in stratified epithelia based on shape of cells in apical layer
- Pseudostratified epithelium:
- All cells are attached to the basement membrane, but not all cells extend to the free surface.
- The nuclei, being at dissimilar levels, give the epithelia a stratified appearance.
By shape of the cells
- Squamous cells: thin or flattened cells
- Cuboidal cells: cell width and thickness mostly like (cube-shaped)
- Columnar cells: cells are taller than wide (column-shaped).
- Transitional: shape of cells "goes through a transition":
- When the organ (e.yard., bladder) is relaxed, cells announced cuboidal.
- When the organ is distended, cells flatten.
By function
Note that there are tissues that have both:
- Covering epithelium: line the cavities or organs
- Glandular epithelium: secretory
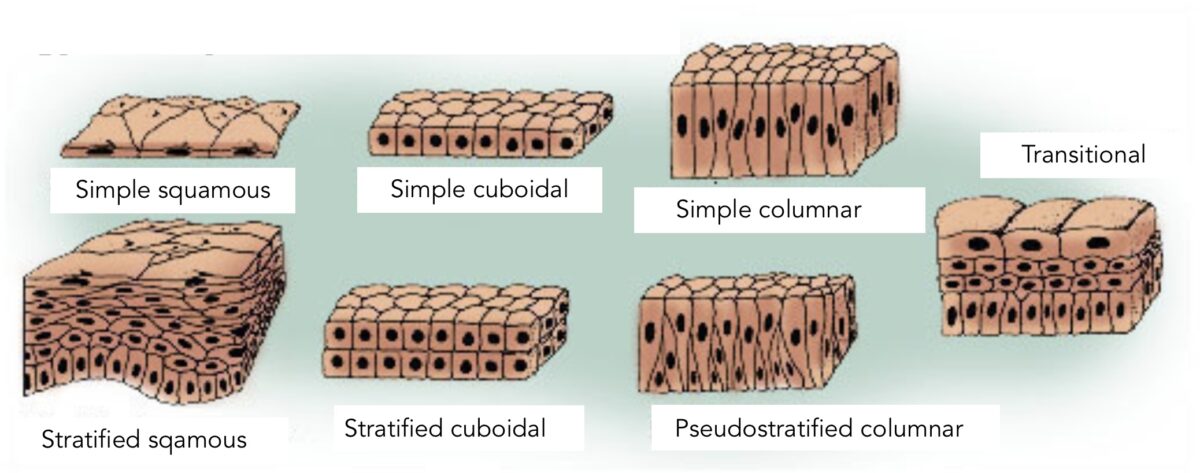
The types of epithelia:
The differentiation and classification of the types are based on the shape of the cell and the layers. Simple epithelium indicates 1 layer of cells. Stratified epithelium indicates multiple layers. Pseudostratified epithelium gives a false impression of > 1 layer attributable to unlike nuclei levels. Transitional epithelium is a type in which the shape of cells "go into transition" depending on the organ function (distention versus relaxation, equally seen in the urinary bladder).
Simple Epithelium
Uncomplicated squamous epithelium
- Characteristics:
- Single layer of flattened cells
- Disc-shaped nuclei (most prominent structure)
- Sparse cytoplasm
- Typically plant in lining of vessels, regulating passing substances to the tissue(south)
- Located in:
- Air sacs/alveoli of lungs
- Lining of the heart
- Claret vessels and lymphatic vessels
- Renal loops of Henle
- Cornea
- Special naming:
- Endothelium: uncomplicated squamous epithelium lining blood vessels and lymphatic vessels
- Mesothelium: uncomplicated squamous epithelium establish in big torso cavities (secreting serous fluid)
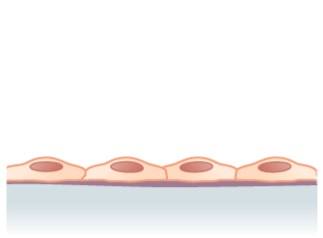
Structure noted in simple squamous epithelium (single layer of flattened cells)
Image: "Simple squamous epithelium" by Phil Schatz. License: CC Past 4.0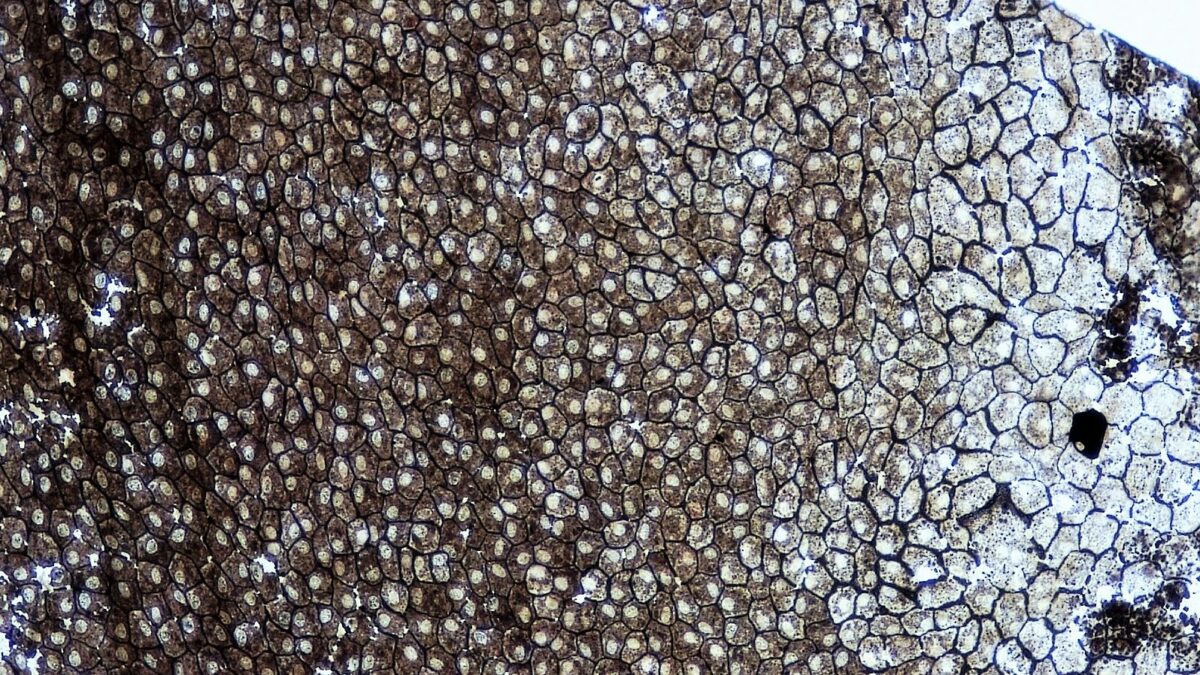
A whole mount of simple squamous epithelium
Image: "Epithelial Tissues Simple Squamous Epithelium" by Berkshire Customs Higher Bioscience Paradigm Library. License: CC0 i.0Simple cuboidal epithelium
- Single layer of cube-like cells
- Cuboidal shape allows increased mitochondria and other organelles needed for functions such as agile send, secretion, and absorption.
- Found in:
- Ducts and secretory portions of glands
- Kidney tubules
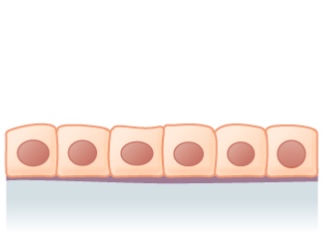
Elementary cuboidal epithelium: 1 layer of cuboidal cells
Image: "Unproblematic cuboidal epithelium" by Phil Schatz. License: CC Past 4.0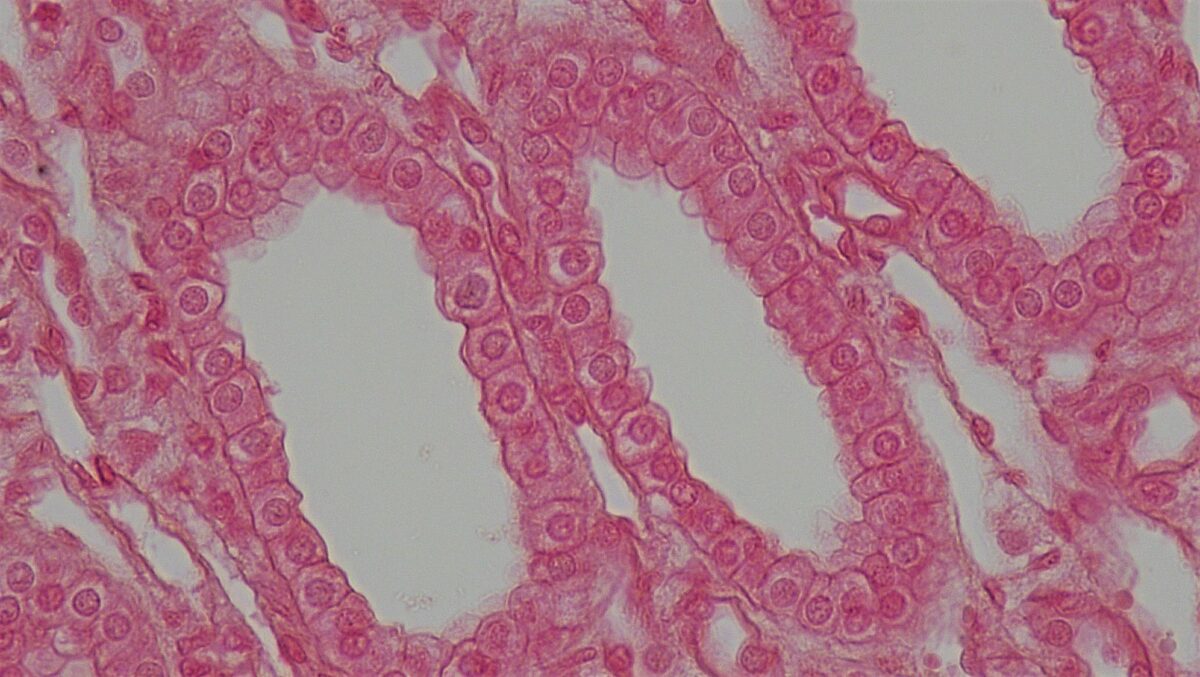
Cross section of a kidney tubule showing a layer of cuboidal cells
Image: "Epithelial Tissues Simple Cuboidal Epithelium" by Berkshire Community College Bioscience Image Library. License: CC0 1.0Simple columnar epithelium
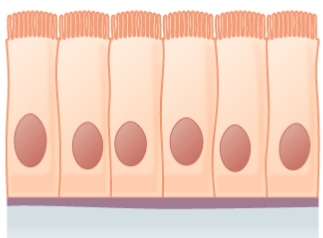
- Single-layer tall cells
- Oftentimes with cilia or microvilli
- Mostly involved in assimilation and secretion
- Plant in:
- Ciliated epithelium in the bronchi, fallopian tubes, and uterus
- Smooth (nonciliated) epithelium in the digestive tract
- Lining of the gallbladder
Elementary columnar epithelium:
Shown is a layer of columnar cells with cilia
Simple columnar epithelium lining the intestinal tract
Image: "Epithelial Tissues Uncomplicated Columnar Epithelium" by Epithelial Tissues: Simple Columnar Epithelium. License: CC0 1.0Pseudostratified, Stratified, and Transitional Epithelia
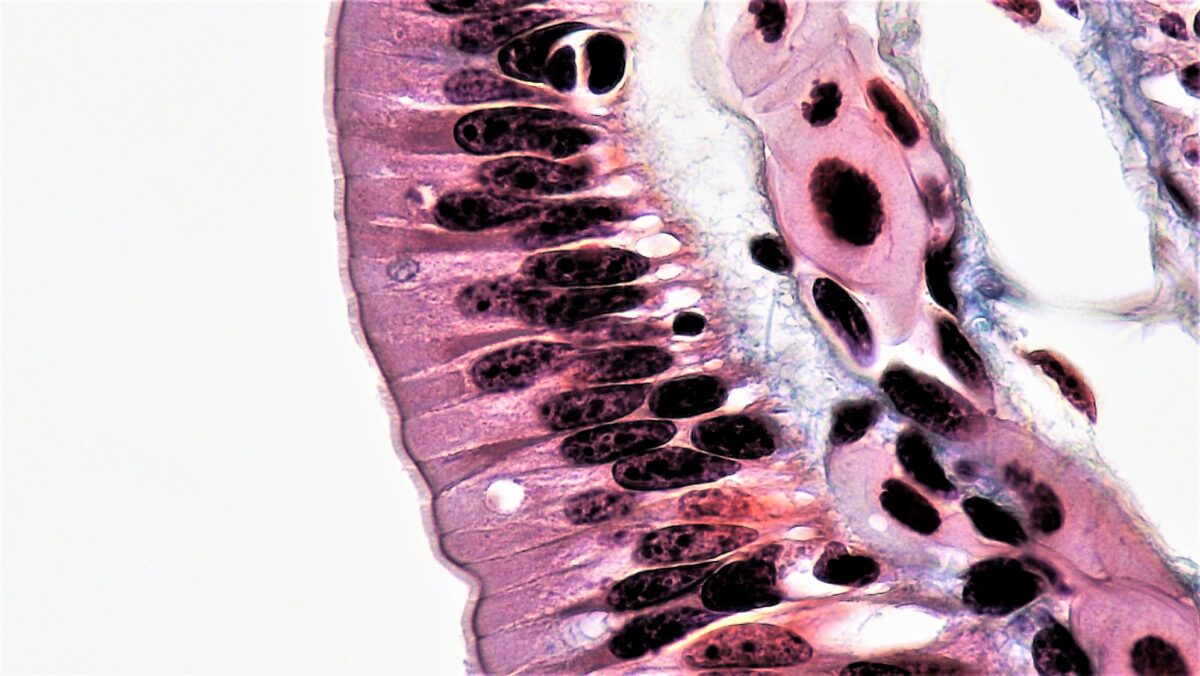
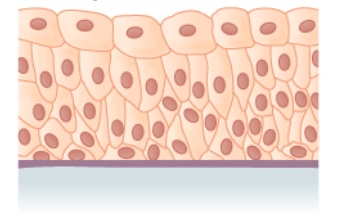
Pseudostratified columnar epithelium
- Characteristics:
- Cells vary in height, with all cells resting on the basement membrane only but some reaching all the mode to the upmost surface.
- Nuclei placed at different heights
- Some accept cilia.
- Functions in secretion and absorption
- Establish in:
- Ciliated epithelium of the trachea
- Part of the upper digestive tract
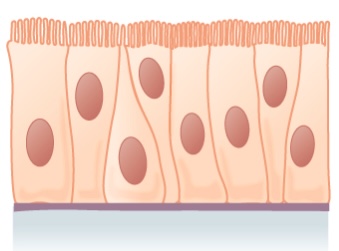
Pseudostratified epithelium:
Shown is a single layer of columnar cells, with varying levels of nuclei
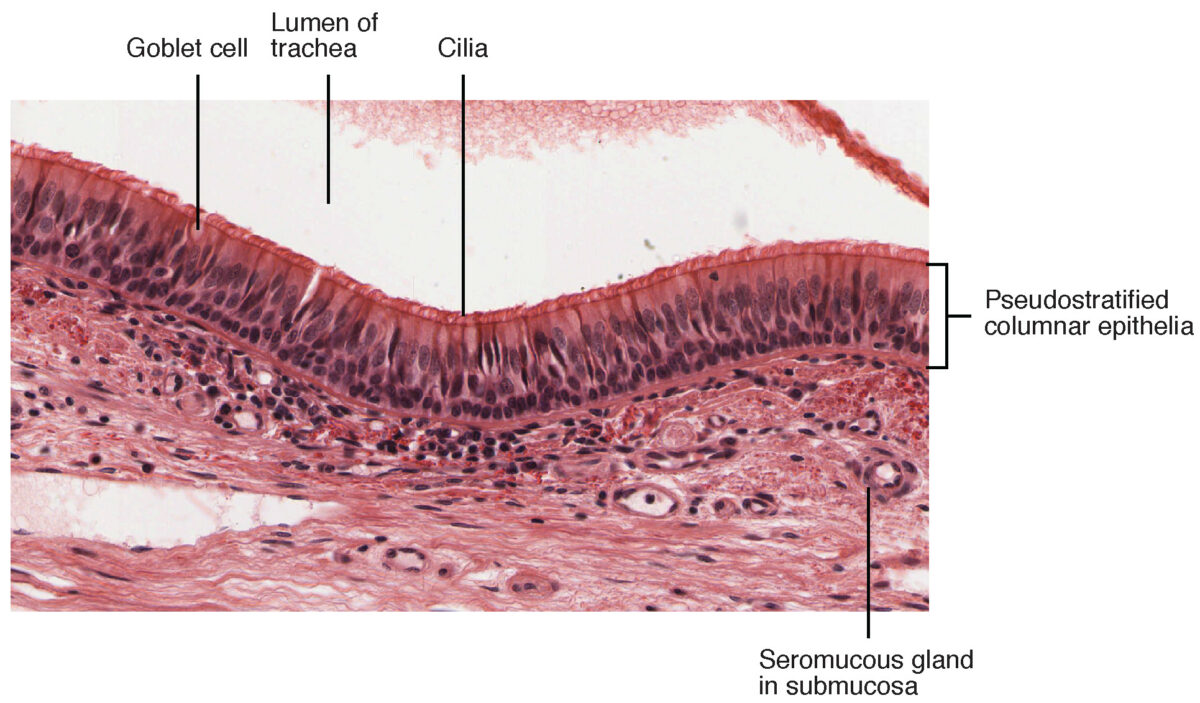
Pseudostratified columnar epithelium found in the trachea
Prototype: "Cross-department of pseudostratified columnar epithelium" past OpenStax Higher. License: CC BY three.0Stratified squamous epithelium
- About widespread of the stratified epithelia
- Composed of several layers, providing protective function
- Free surface cells are squamous.
- Deeper layer cells are cuboidal or columnar.
- Establish in areas subjected to article of clothing and tear
- Found in:
- Skin, which is keratinized or filled with keratin:
- These cells will lose the organelles and nuclei as they flatten and accumulate keratin.
- Cells move toward the surface, becoming metabolically inactive and are sloughed off.
- Esophagus, mouth, vagina, which accept nonkeratinized cells (retain the nuclei)
- Skin, which is keratinized or filled with keratin:
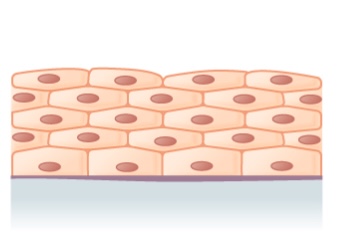
Illustration of stratified squamous epithelium (multiple layers)
Paradigm: "Stratified squamous epithelium" by Phil Schatz. License: CC BY iv.0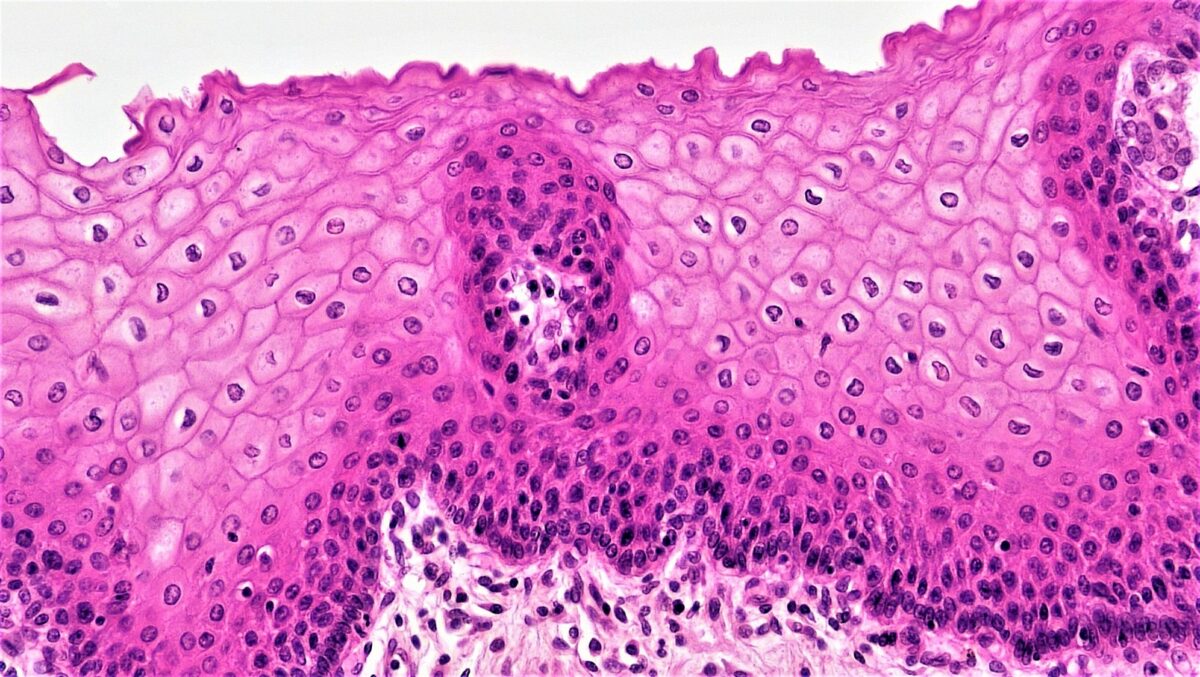
Histologic picture of stratified squamous epithelium
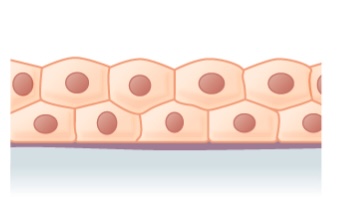
Image: "Epithelial Tissues Stratified Squamous Epithelium" by Berkshire Community College Bioscience Image Library. License: CC0 ane.0Stratified columnar epithelium and stratified cuboidal epithelium
- Both are rare and have limited distribution.
- Stratified columnar epithelium:
- Secretory and protective function
- Found in:
- Male person urethra
- Some glandular ducts
- Stratified cuboidal epithelium is institute in ducts of large glands (e.g., sweat glands, mammary glands).
-
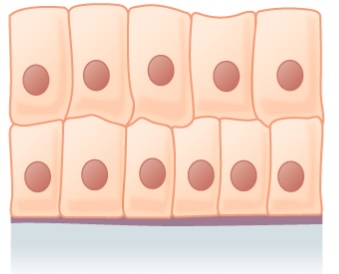
Stratified columnar epithelium
Image: "Stratified columnar epithelium" by Phil Schatz. License: CC By 4.0 -
Stratified cuboidal epithelium
Prototype: "Stratified cuboidal epithelium" by Phil Schatz. License: CC By 4.0
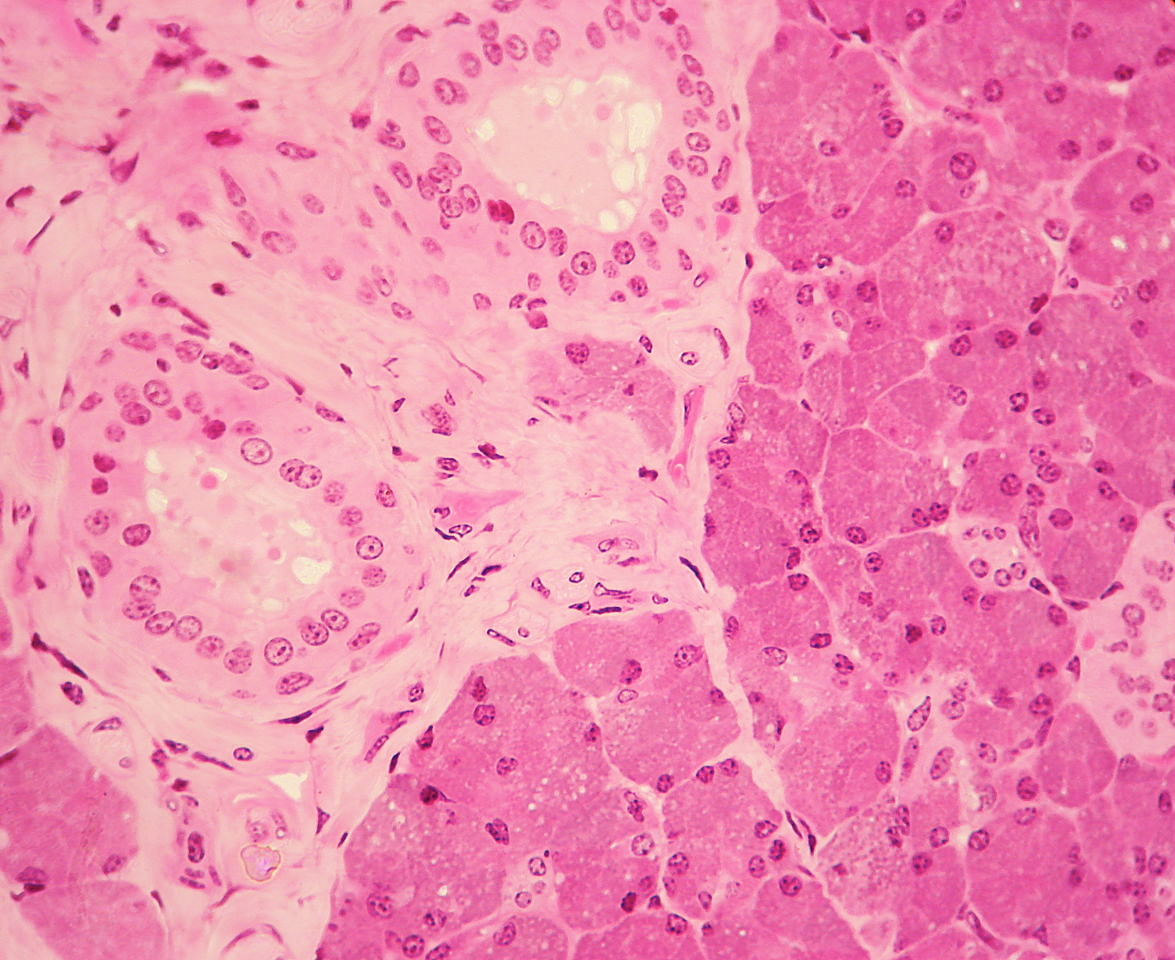
Stratified cuboidal epithelium (seen on the left) is visible in a duct surrounded past connective tissue in the parotid gland.
Epitome: "WVSOM Parotid Gland1" past Wbensmith. License: CC By iii.0Transitional epithelium
- Characteristics:
- Surface layer of umbrella cells (dome-like cells)
- Allows for stretching of the organs as they distend
- Urothelium: transitional epithelium in the urinary tract
- Establish in:
- Urinary bladder
- Urethra
- Ureters
Transitional epithelium
Image: "Transitional epithelium" by Phil Schatz. License: CC BY iv.0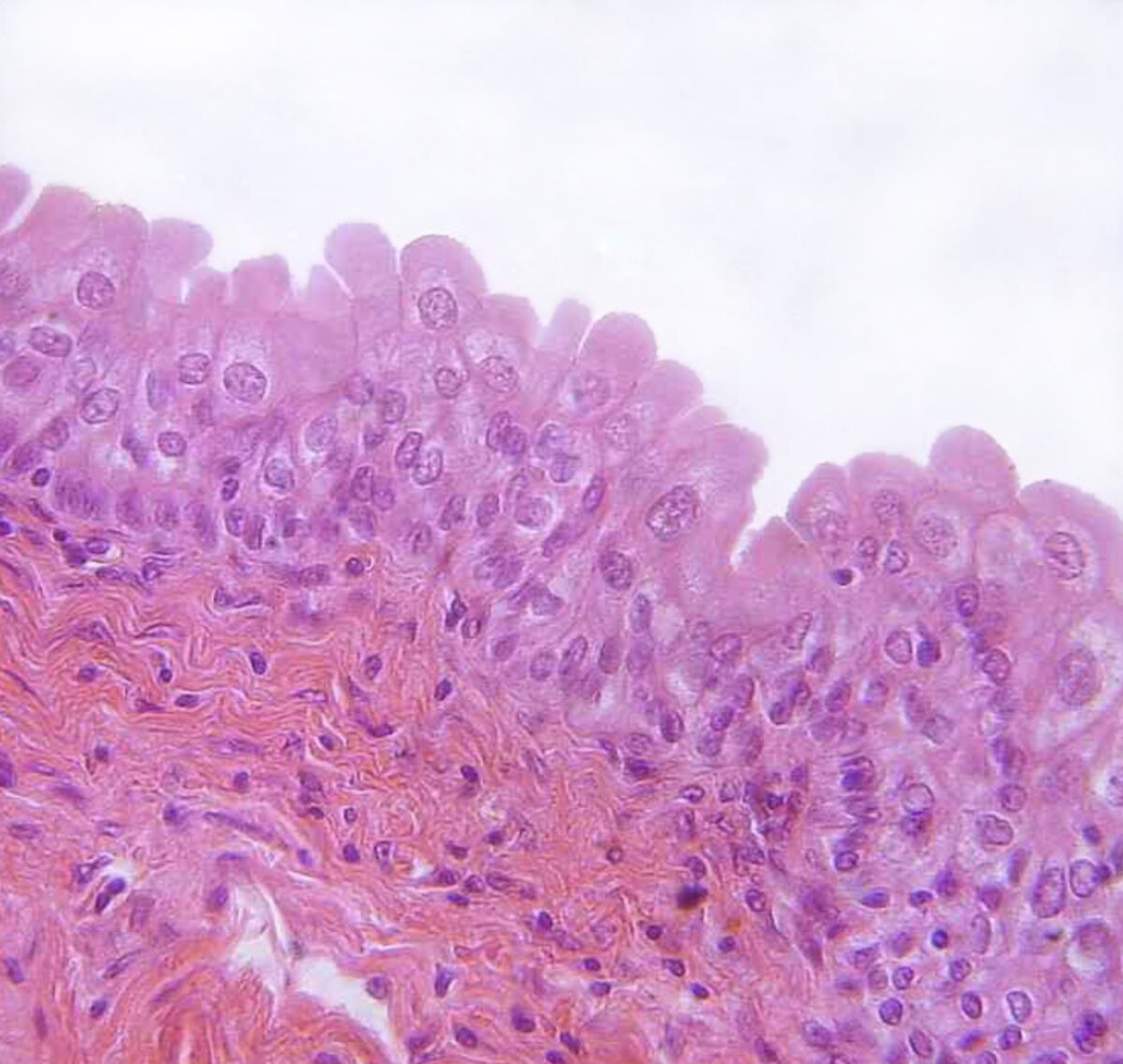
Transitional epithelium found in the urinary bladder
Image: "urinary bladder, urothelium, haemalum-eosin stain" past Polarlys. License: CC BY two.vClinical Relevance
- Ichthyosis: dermatologic disease in which aberrant keratinization occurs. Ichthyosis is caused by an autosomal dominant mutation in the filaggrin gene, which results in pare bulwark dysfunction. Clinical presentation features rough, dry, and scaly peel, with symptoms worsening during cold, dry months. The diagnosis is normally clinical simply ofttimes aided with a skin biopsy showing hyperkeratosis and a diminished stratum granulosum.
- Transitional prison cell carcinoma: malignancy affecting the urinary float. Transitional prison cell carcinoma is the most common cancer involving the urinary organisation. The predominant histologic type is urothelial (transitional prison cell) carcinoma in the United states and Europe. Take chances factors include genetics, smoking, opium employ, and occupational carcinogen exposure. Presentation is unremarkably with painless hematuria, and the diagnostic approach includes cystoscopy, urine cytology, and biopsies. Transurethral resection of bladder tumor, radical cystectomy, and chemotherapy are amongst the handling options, which depend on the phase.
- Barrett's esophagus: replacement of stratified squamous epithelium with gastric columnar epithelium in the esophagus caused by chronic GERD. This is associated with an increased risk of esophageal adenocarcinoma. Esophagogastroduodenoscopy would show proximal displacement of the squamocolumnar junction (Z-line) from the gastroesophageal junction (GEJ). Biopsies reveal columnar epithelium and goblet cells in the distal esophagus. Treatment is with proton pump inhibitors and lifestyle modifications.
- Cervical cancer: very common cancer affecting women. Nigh cases of cervical cancer are due to HPV. The region around the external os is lined by nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium continuous with that of the vagina. This area meets the mucus-secreting columnar epithelium of the endocervix in the transformation zone. Exposure of the transformation zone to HPV can pb to squamous differentiation into squamous intraepithelial lesion (leading to squamous jail cell carcinoma). The endocervical columnar epithelium tin can develop into glandular intraepithelial lesions (which tin progress to adenocarcinoma).
Source: https://www.lecturio.com/concepts/surface-epithelium/
0 Response to "what two words are used to classify epithelium in terms of the number of cell layers"
Post a Comment